Visibility trials for drone detection
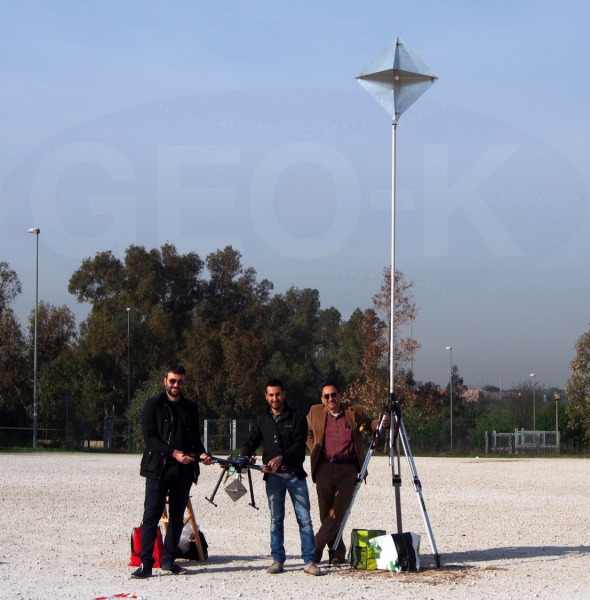
GEO-K, collaborating with the RADARLab of the Electronic Department of the “Tor Vergata” University, is performing drone’s visibility trials making use of its exa-rotor high-quality carbon fiber frame drone, an X-band radar and a corner reflector with known RCS. These tests are going to show the detection capability of Radar Systems, retrieving also the radiometric characterization of commercial drones.
The term “drone” is commonly used to indicate an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV), or an aircraft which is remotely controlled by a ground-based operator. During the last years, drones have increasingly captured the interest of entrepreneurs and investors alike as a means to take over certain tasks, such as commercial, scientific, recreational and agricultural applications, surveillance services, product deliveries and aerial photography. Recently, the growing use of drones also among common people is due to the possibility of purchasing them at a lower price, increasing concerns about their use. Last year, in fact, more than 3456 incidents involving drones were recorded, compared with only 1237 in 2015, PA news agency reported. Moreover, drones have been reported to be used for criminal purposes and illegal actions. The problem of how drones can be detected and controlled over a limited area is directly rising up. Radar sensors are suitable to detect big objects, but drones may also be seen.